
In the 20th century, local economies in these states specialized in large-scale manufacturing of finished medium to heavy industrial and consumer products, as well as the transportation and processing of the raw materials required for heavy industry. The Great Lakes megalopolis shown in orange is associated with the Rust Belt. beginning in the 1980s when it was commonly contrasted with the Sun Belt, which was surging. The term "Rust" refers to the impact of deindustrialization, economic decline, population loss, and urban decay on these regions attributable to the shrinking of the once-powerful industrial sector especially including steelmaking, automobile manufacturing, and coal mining. These regions experienced and, in some cases, are continuing to experience the elimination or outsourcing of manufacturing jobs beginning in the late 20th century. GDP peaked in 1953 and has been in decline since, impacting certain regions and cities primarily in the Northeast and Midwest regions of the U.S., including Buffalo, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Detroit, Jersey City, Newark, Pittsburgh, Rochester, Toledo, Trenton, Youngstown, and other areas of New Jersey, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and Upstate New York. manufacturing sector as a percentage of the U.S. The Rust Belt is a region of the United States that experienced industrial decline starting in the 1950s. The company filed bankruptcy in 2001 and was dissolved in 2003. In 1982, however, Bethlehem Steel suspended most of its manufacturing. Detroit emerged as the center of the American automobile industry, and became the home of the so-called Big 3 automakers: Ford, General Motors, and Chrysler.The rusting steel stacks of Bethlehem Steel in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, one of the world's largest manufacturers of steel for most of the 20th century. Cleveland became the home of the Standard Oil Company in the 1860s, and was also a notable transportation hub. Buffalo became the largest grain port in the world. Pittsburgh was known as a center for steel manufacturing, dating all the way back to the U.S. Later on, General Motors built a plant in the city, as did Bethlehem Steel. Baltimore became a mecca for the production of metal and ship-building. In fact, it became one of the largest railroad centers in the country, and served as a base for the manufacture of freight and passenger railroad cars. Other important cities in what was once the focal point of American industry include Baltimore, Maryland Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Buffalo, New York Cleveland, Ohio and Detroit, Michigan. cities that became part of America’s Factory, and later, part of the Rust Belt. The last of the old time rust belt steel mills that is still in operation today in Cleveland, Ohio.Ĭhicago was just one of the major U.S. The Illinois and Michigan Canal, which links Lake Michigan with the Mississippi River, helped make the Windy City the transportation center of Illinois by the 20 th century. For example, Chicago’s proximity to the Mississippi River and Lake Michigan enabled a steady flow of both goods and people.
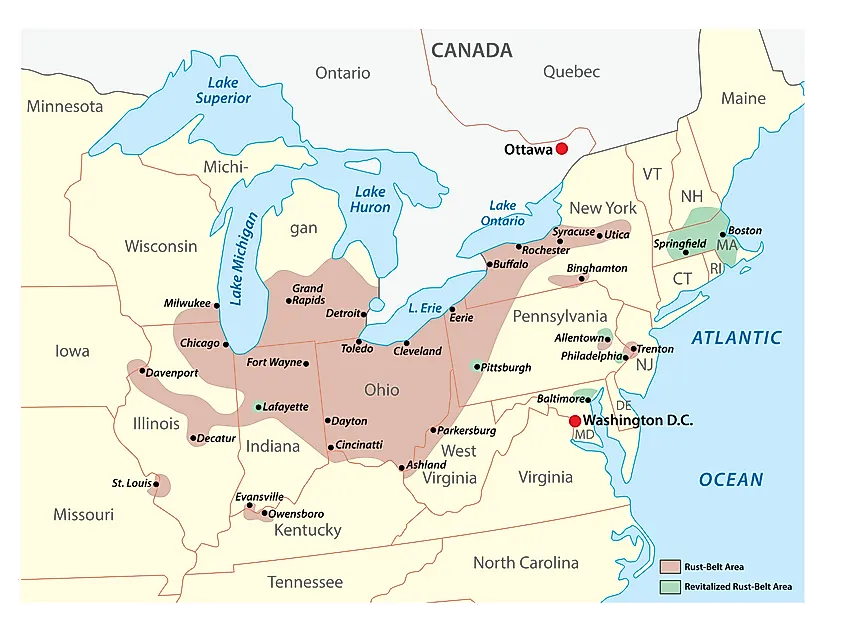
In addition, the area that is now referred to as the Rust Belt had a very good transportation network in the form of waterways. There was also a plentiful supply of labor in the region, as people immigrated from Europe and the U.S. The region became America’s industrial center, owing in large part to its natural resources, especially iron ore and coal. All these nicknames denoted the region’s importance for the U.S. In the 19 th and early-to-mid-20 th century, what is now known as the Rust Belt was defined by other nicknames, including Factory Belt, Steel Belt, or Manufacturing Belt. Ever since, the term “Rust Belt” has been used to refer to the once-prosperous industrial heartland of the U.S. In 1984, Democratic presidential candidate Walter Mondale called this declining region the rust bowl, though he was misquoted by the media, who thought that he said rust belt.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
